Google was initially a simple search engine that would help people find information online, founded in 1998 by Larry Page and Sergey Brin. It was the uniqueness of its algorithm, PageRank, which ranked websites based on relevance and trustworthiness, that set Google apart. Over time, Google’s search capabilities expanded and became the most widely used search engine in the world, handling billions of searches daily.
Google’s success is mostly because its search algorithms keep changing and getting better. These algorithms decide how web pages show up in search results. By making things more accurate and improving user experience, Google’s algorithms have changed the way we use the internet. Nowadays, these algorithms even use cool tech like artificial intelligence to give us better, more personalized search results.
What are Google algorithms?
Google algorithms are very complex systems that help rank web pages in the search results. They check all kinds of stuff- keywords, quality of content, user experience, and backlinks to figure out how relevant the page is to a specific search. In essence, they wanna give users the best, most useful, and top-notch results. Google has developed various algorithms, such as PageRank, Panda, Penguin, and RankBrain, over time. All of these evolved into machine learning and artificial intelligence. The updates are for the betterment of search accuracy, to combat spam, and for a better user experience on the web.
Father of Google’s founding search engine history
Thus, in 1995, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, two PhD students at Stanford, began collaborating on this research project to make internet searches better. They realized that the search engines out there weren’t really cutting it when it came to giving accurate and relevant results. Instead of just slapping together search terms with whatever content, Larry and Sergey thought there had to be a smarter way to rank pages based on how important and relevant they were for the user.
Their solution, which eventually became Google, was the PageRank algorithm. It looked at how many and what quality links pointed to a web page, rather than just the words on the page itself. They realized that a page with many links from trusted and authoritative sources was probably more important than one with fewer links. This revolutionary approach made Google’s search results much more accurate and useful than those from other existing search engines.
The idea of the page and Brin
In 1998, Page and Brin formally launched Google from a garage in Menlo Park, California. They had an idea to organize the world’s information in such a manner that it would be accessible and useful everywhere. This simple yet powerful idea quickly picked up steam, and Google became one of the world’s most popular search engines. Their emphasis on user experience and the strength of the PageRank algorithm were key factors that contributed to Google’s rapid growth and dominance in the tech industry.
What inspired Larry Page and Sergey Brin to choose the name “Google”?
Larry Page and Sergey Brin, the founders of Google, were inspired by a mathematical term when choosing the name “Google.” The name comes from the word “googol,” which refers to the number 1 followed by 100 zeros. They chose this name because it symbolized the vast amount of information they wanted to organize and make accessible on the web. Their goal was to create a search engine capable of handling an immense amount of data and delivering accurate, useful results. The name “Google” was a playful twist on “Google,” reflecting their ambition to revolutionize search and organize the world’s information on a massive scale. The name also suggested the company’s potential to grow and expand, just like the enormous number it was named after.
The Rise of Google Search
1. The First Version of the Search Engine
Back in 1998, Google rolled out its first search engine. Unlike all the other ones back then, it used this cool thing called PageRank, which ranked websites by how good their links were and how many there were, instead of just counting keywords. This helped Google give more accurate and relevant results. Plus, the search engine had this super simple and clean design that made it stand out from the rest, which was all stuffed with ads and random features.
2. Improved User Experience
Google focused on the delivery of a user-friendly experience. The outcome of the search was quick and relevant, and the simple interface allowed the users to easily find what they wanted. The simplicity and effectiveness of Google made it the favorite of internet users within a very short time. It was faster and much more efficient compared to its competitors because it did not have complex and slow interfaces.
3. Word-of-mouth marketing and early growth
So, as people began to realize how great Google’s search results were and how easy it was to use, the word spread fast. People began telling their friends and coworkers about Google. This organic growth helped Google get going early on. By the early 2000s, millions of people were using Google every day, and it was quickly turning into the most popular search engine out there. The good vibes from user experiences helped it rise.
4. Adding other features
Google didn’t stop at being just a search engine. Over time, it began adding new features and services to improve the overall user experience. Google introduced features like Google Images, Google News, and Google Maps, further increasing its usefulness. These services complemented the search engine, making Google a one-stop shop for various needs. The company’s ability to innovate and expand kept users engaged and helped Google maintain its dominance in the search engine market.
5. Rapid Growth and Market Dominance
By the year 2000, Google was processing over a billion searches a month. Its focus on continuous improvements and user satisfaction led to massive growth. As more users adopted Google and experienced its efficiency, the company expanded its market share. Google’s knack for giving spot-on, relevant, and quick results is what helped it beat out the competition like Yahoo and AltaVista, making it the top search engine and turning it into a tech giant with worldwide clout.
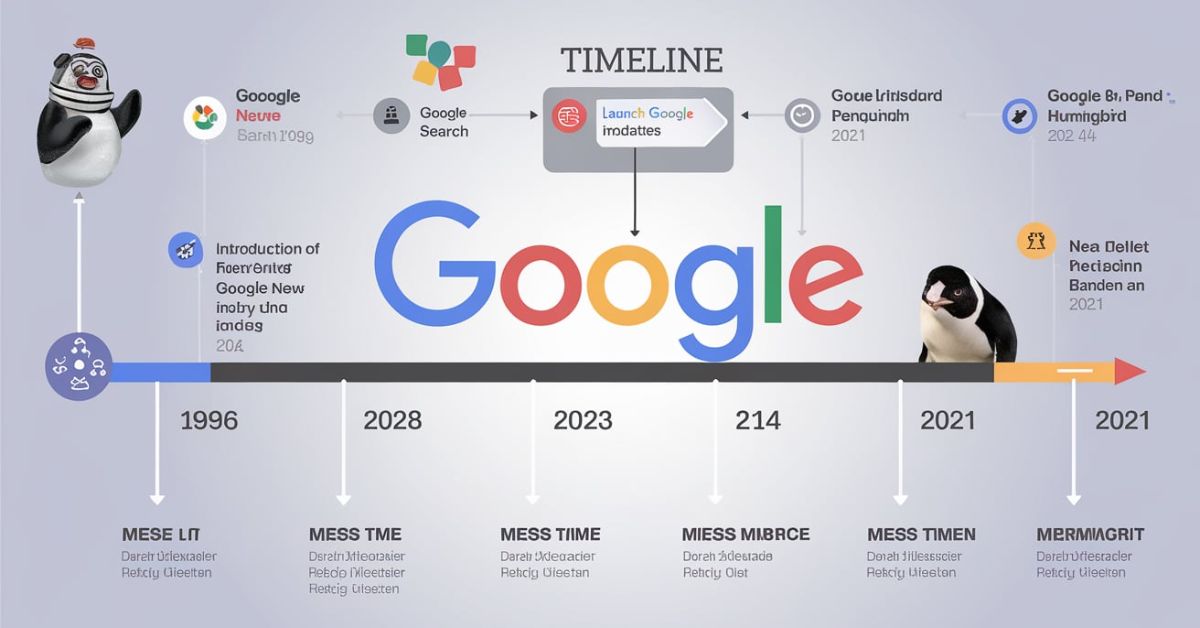
Major Algorithm Updates
1. PageRank Algorithm (1998)
The first crucial algorithm was created by Larry Page and Sergey Brin and was named PageRank. It ranked web pages according to the number and quality of links pointing to those pages. In other words, pages with more high-quality links are likely to be important. That was the reason this algorithm laid the foundation of Google’s search engine that delivers relevant results through analysis of the web structure. Google differentiated itself in delivering search results as more accurate compared to others.
2. Google Toolbar 2000
In 2000, Google introduced the Google Toolbar. This tool was used to allow users to search Google from their browser directly. The update made Google more accessible to the public, providing people with a quicker means of searching without opening the website. The toolbar also offered page ranking and easy navigation. Introducing the toolbar was an important step in making Google a household name and cementing its place as a leading search engine.
3. Florida Update 2003
In 2003, Google’s very first important update was the Florida update. It targeted spammy websites, which had been using keyword stuffing and overlinking in mass to rank higher in search results. As a result, Google wanted to improve the quality of its search results and penalized websites using these manipulative practices. This update caused many websites to severely drop in rank, and it started Google’s long and ongoing battle against spam and low-quality content.
4. Panda Update (2011)
In 2011, Panda was released by Google to punish those websites that offered thin or copied content. Instead, the system was intended to reward those websites with unique content that can better facilitate users. Those sites with keyword stuffing, grammatical errors, and shallow content are ranked lower. Panda focused more on quality instead of quantity to encourage webmasters to make valuable and informative content for their users.
5. Penguin Update (2012)
The Penguin update, which was launched in 2012, targeted spammy link-building practices that violated Google’s guidelines. Websites that bought links or participated in link farms were penalized. Google wanted to ensure that links were earned naturally, based on content quality and authority. Penguin pushed webmasters to focus on earning organic, relevant backlinks rather than relying on manipulative strategies to rank higher in search results.
6. Hummingbird Update (2013)
So, back in 2013, Google dropped the Hummingbird update, which was all about getting better at understanding natural language and what users meant when they searched. Hummingbird helped Google deal with complicated questions way better, so it could give back results that were more on point and relevant. It was a big change from just matching exact keywords to figuring out the meaning behind words and phrases. This update made Google a lot smarter and way better at tackling conversational queries and long-tail searches.
7. Mobile-Friendly Update (2015)
The Mobile-Friendly Update, which was also known as “Mobilegeddon,” was launched in 2015. This update was supposed to enhance the search experience for users who accessed the web through mobile devices. Websites that were not optimized for mobile were penalized, while those that were mobile-friendly saw a boost in rankings. This update reflected the growing importance of mobile usage, as more people were accessing the web through smartphones and tablets, signaling the need for responsive and mobile-optimized websites.
8. RankBrain Update, 2015
In 2015, Google launched RankBrain, a machine learning-based algorithm that helped Google understand search queries better. RankBrain processed millions of queries and learned over time how to improve results, especially for complex or unfamiliar searches. It used artificial intelligence to interpret the meaning behind user queries and provide the best possible results. RankBrain helped Google refine its search results by focusing on the intent behind each query rather than just the keywords.
9. Pigeon Update (2014)
So, the Pigeon update came out in 2014, and it was all about making local search results better. It really changed how Google handled location-based searches, which meant local businesses and services popped up more in the search results. This update affected search results for businesses in certain areas, making local listings and maps more important. Pigeon made it way easier for folks to find local info that actually mattered, so local search results got way more accurate and helpful.
10. Fred Update (2017)
Fred update was released by Google in 2017, targeting sites with low-quality content and too many ads. It penalized sites that were monetarily focused rather than user-experience-oriented, often full of ads and clickbait. Fred improved the quality of content and reduced the number of sites that manipulated search rankings with poor-quality material. Reward for websites with useful, well-structured content, and penalties to sites that are monetized by advertisements.
11. BERT Update (2019)
Google has developed BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers), a significant update to the search engine with the aim of better-understanding words in a query in context. This would help Google understand conversational searches and interpret words in context, which will lead to better results. Google can now understand complex, long-tail queries with multiple meanings, making it possible to give users more natural and accurate responses to their searches.
12. Core Updates (Ongoing)
Google regularly updates its core algorithm, which means broad changes to the search results overall quality. It is not targeting specific issues but rather improving Google’s ability to rank pages on quality, relevance, and user experience. Each core update can cause a fluctuation in search rankings, as websites that better meet Google’s evolving standards are rewarded, while sites with lower-quality content or practices may see a decline.
So, way back in 2018, Google said it was going to focus the ranking and indexing on the mobile versions of the websites. The reason for this is that very many people were surfing the internet on their smartphones and tablets. If the website isn’t mobile-friendly or has a bad mobile experience, then it drops down in the rankings. Mobile-first indexing underlined the necessity of responsive design and mobile optimization, so a website had to prioritize mobile user experience to remain good in search rankings.
14. Medic Update 2018
Medic updates rolled out in 2018 focused mainly on health-related websites and those in YMYL categories, which include topics like finance, health, and legal advice. It has tried to improve the quality of content on those sensitive topics by promoting E-A-T websites. That is, the update was more about minimizing misinformation as well as improving the quality of content that people used for important decisions in areas like health and finance.
15. Google Passage Ranking (2020)
So, back in 2020, Google rolled out this thing called Passage Ranking. It lets the search engine rank specific sections of a page instead of just the whole page. This change really boosted how well the search engine could get and serve up spot-on answers for those more detailed or specific questions. For instance, if a page had a paragraph that answered a specific question, that passage could now be ranked independently, making it more likely to appear in search results for a user’s query.
Evolution of Search Features
1. Knowledge Graph
Knowledge Graph was introduced in 2012 and was a major step forward in improving the search experience. It allowed Google to give you better, more useful results by figuring out how people, places, and things are connected. So when you look up something, the Knowledge Graph pops up a box on the right side of the results page with important info, quick facts, images, and links that are related. This feature helps people find answers faster without having to click through a lot of links, which makes Google’s search results much more helpful and informative.
- Featured Snippets In 2014, Google introduced Featured Snippets to deliver users quick answers right at the top of search results. Snippets show a short, direct answer to a question along with where it came from, so the user doesn’t have to click over to a website. Featured snippets are there to give you quick and handy information straight on the search page, so you can find answers without any hassle. This is super useful for stuff like “how to” guides or simple fact questions, making it easier and quicker for users.
- Voice Search and Mobile Optimization With everyone using smartphones and smart devices now, Voice Search totally changed the game. Google began to optimize its search engine for voice searches. These often include longer sentences that sound conversational, such as voice queries that enable people to search hands-free with more conversational questions using natural language. The company continued optimizing websites in 2015 through Mobile Optimization: sites must now be mobile-friendly and responsive. With more and more humans accessing the web on mobile devices, Google favored mobile-first indexing as a means of rewarding sites with mobile-friendly designs for improving the overall search experience across all devices.
AI and the Future of Google Search
1. Generative AI Introduction
Generative AI is changing the way Google Search works by allowing it to generate new content instead of just fetching existing data. This technology can produce direct answers, summaries, and even creative content, making search results more dynamic and informative. For instance, Google’s AI can provide tailored answers to complex queries, saving users time by offering relevant, generated content directly on the search page.
2. Improved Search Accuracy
AI helps Google get what users want, making searches way more accurate. Machine learning doesn’t just look at keywords; it digs into the context behind them, so Google can give back results that fit what the user is after. This shift moves away from needing exact keyword matches and leans more into the meaning of what people are asking, making search quality way better.
3. Personalized Search Results
Google’s AI will continue to refine the personalized search experience based on user behavior, preferences, and past searches. This will eventually allow Google to deliver highly customized results based on a user’s interests. Personalized experiences may change based on location, search history, or even time of day, so users will get the most relevant information possible.
4. Voice and Conversational Search
With AI, voice search has become the new norm. Users expect to speak naturally to search engines and get accurate, relevant results. AI-powered voice recognition and processing allow Google to better understand conversational language, providing answers that are more fluid and natural. This shift will make voice search a key part of the future of Google Search.
5. Improved Content Creation and Summarization
AI is going to be a huge deal for cranking out summaries and pulling out important information from lengthy articles. So, when people are looking for something specific, generative AI can mix content from different sources and dish it up as a short, clear summary, which saves people from slogging through a bunch of articles to find what they need.
6. Visual and Multimedia Search
AI will further enhance Google’s ability to search and display visual and multimedia content. Through advancements in image recognition and computer vision, Google can analyze images, videos, and other media to provide better search results. This will allow users to search for content using images instead of text, making the search process more intuitive and interactive.
7. Continuous Learning and Adaptation
As Google Search evolves, AI will continuously learn from user interactions, improving its results over time. This means that Google’s algorithms will get smarter, adapting to trends, changing language, and new content. As AI becomes more advanced, Google’s search engine will be able to provide answers that are more precise and relevant to individual users, enhancing the search experience for everyone.
Staying Updated with Google’s Algorithm Changes
1. Monitor Google’s Official Channels
The best way to keep track of the changes that Google has for its algorithm is to monitor their official material, especially the Google Search Central Blog and the Google Webmaster’s Twitter account. Most of the important updates and announcements are released there. With continuous monitoring of the above-mentioned channels, you will be able to know what is happening on the search engine and how it can affect your site.
2. Monitor Your Search Performance Regularly
It’s important to keep an eye on your website’s search performance, especially after Google rolls out updates. Use tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console to track any sudden changes in traffic, rankings, or visibility. If you notice a drop in performance, it could be due to an algorithm update. Regular monitoring helps you react quickly and adjust your SEO strategy when needed.
3. Engage with SEO communities and professionals
Forums, online groups, and social media are great places to pick up information about algorithm changes. Sites like Search Engine Journal, Moz, and Search Engine Land usually break down updates well. Being part of these communities lets you see how updates affect things, swap ideas, and learn from what others in the SEO world have gone through.
4. Keep up with the latest SEO best practices
Google is always changing the way it ranks websites, so it’s really important to keep up with the latest SEO best practices. Make sure your site checks all the boxes for Google’s guidelines on content quality, being mobile-friendly, and loading fast. As Google updates its algorithms, there might be fresh strategies to boost your rankings, like focusing on user experience, keeping your content relevant, or nailing that technical SEO. 5. Test and Adapt Your Strategies
So, right after an algorithm update, you should check how your website is doing and tweak your SEO strategies. Try out different things to figure out what helps boost your rankings. If you spot any problems post-update, like dropping ranks for some keywords, it would definitely be worth adjusting your content, links, or the entire site layout to improve results and catch up with what Google’s changing.
Conclusion
Google has transformed how we obtain and utilize information by growing from a basic search engine into a multinational technological behemoth. Its search algorithm began emphasizing links and relevancy in 1998, making it easier for visitors to locate what they were looking for. To enhance user experience by delivering more precise and pertinent results, Google has updated its algorithms several times over the years, including PageRank, Panda, Penguin, and RankBrain. Google’s algorithms are still evolving today, taking into account elements like article quality, mobile optimization, and user intent. Google continues to dominate search engines in spite of obstacles and competition, continuously improving its technology to satisfy the demands of a dynamic online environment.